Author Affiliations
Abstract
School of Instrumentation Science and Opto-electronics Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
A superluminescent diode (SLD) as an alternative of laser is used to detect optical rotation for atomic spin precession. A more uniform Gauss configuration without additional beam shaping and a relatively high power of the SLD have a potential for atomic magnetometers, which is demonstrated in theory and experiments. In addition, the robustness and compactness enable a more practical way for optical rotation detections, especially for applications in magnetoencephalography systems.
Superluminescent diode atomic magnetometer magnetoencephalography atomic spin precession detection Larmor precession Photonic Sensors
2019, 9(2): 02135
Author Affiliations
Abstract
School of Instrumentation Science & Opto-Electronics Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
The measurement of an extremely small magneto-optical polarization rotation angle with high sensitivity is integral to many scientific and technological applications. In this Letter, we have presented a technique based on Faraday modulation combined with the optical differential method to measure an extremely small polarization rotation angle with high sensitivity. The theoretical and experimental results show that common mode noise is reduced appreciably and signal to noise ratio is enhanced. The effectiveness of this technique has been demonstrated by measuring the Verdet constant of terbium gallium garnet glass and measuring the small polarization rotation angle. A sensitivity of enhancement of one order of magnitude has been achieved using differential detection based on Faraday modulation.
120.5410 Polarimetry 000.3110 Instruments, apparatus, and components common to the sciences 040.1880 Detection Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(8): 081201
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Instrument Science and Opto-Electronics Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
2 International Research Institute for Multidisciplinary Science, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
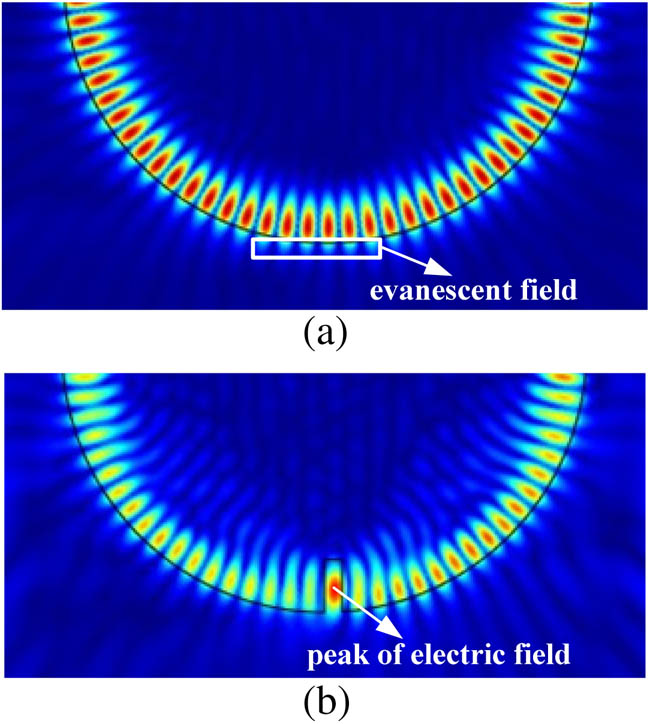
A novel slotted optical microdisk resonator, which significantly enhances light–matter interaction and provides a promising approach for increasing the sensitivity of sensors, is theoretically and numerically investigated. In this slotted resonator, the mode splitting is generated due to reflection of the slot. Remarkably, effects of the slot width and angular position on the mode splitting are mainly studied. The results reveal that the mode splitting is a second function of the slot width, and the maximum mode splitting induced by the slot deformation is achieved with 2.7853×109 Hz/nm. Therefore, the slotted resonator is an excellent candidate for pressure and force sensing. Besides, the influence of the slot angular position on the mode splitting is a cosine curve with the highest sensitivity of 1.23×1011 Hz/deg ; thus, the optical characteristic demonstrates that the slotted resonator can be used for inertial measurements.
Resonators Optical devices Fiber optics components Fiber optics Fiber optics and optical communications Photonics Research
2017, 5(3): 03000194
1 哈尔滨工程大学 核科学与技术学院, 哈尔滨 150001
2 上海交通大学 核能科学与工程学院, 上海 200240
堆芯换料方案的优化是一个典型的组合优化问题, 其搜索空间异常庞大。传统的优化算法很难在如此巨大的搜索空间中寻找出全局最优解。遗传算法以其优良的自适应能力和优化能力, 为组合优化问题提供了一个非常有效的解决途径。采用遗传算法对柱状高温气冷堆堆芯装料方案进行了优化, 并编写了相应程序。为了提高堆物理的计算精度, 堆芯临界计算采用26群输运计算。由于多群输运计算需要大量计算时间, 为此对遗传算法进行了并行优化。为了验证遗传算法对柱状高温气冷堆换料的优化能力, 构造了一个8组件的小型柱状高温气冷堆换料优化基准题。结果表明, 遗传算法在柱状高温气冷堆换料优化问题中具有良好的优化能力和计算稳定性。
遗传算法 换料优化 柱状高温气冷堆 验证 genetic algorithm reloading pattern optimization block-type high temperature gas cooled reactor verification 强激光与粒子束
2017, 29(1): 016002
1 北京航空航天大学仪器科学与光电工程学院, 北京 100191
2 微纳测控与低维物理教育部重点实验室, 北京 100191
3 精密光机电一体化教育部重点实验室, 北京 100191
多层石墨烯具有超宽的光谱吸收范围及独特的光电性能, 是制作下一代光电探测器件的理想材料。 以石墨烯的带间隧穿理论为基础, 提出了一个多层石墨烯纳米带结构的光电探测器模型, 纳米带的两端与源极和漏极相连, 夹在半导体基质和上下栅极之间。 利用这个模型, 建立了多层石墨烯纳米带探测器的光电转换机制, 讨论了上栅极电压不同时探测器的工作原理, 研究了源-漏极间光电流及暗电流与入射光能量的关系, 探讨了探测器的偏置电压, 耗尽层长度以及带隙取值对暗电流的影响, 并分析了不同参数下探测器响应率以及探测率随入射光能量的变化关系。 结果表明, 探测器的响应率随纳米带层数的增加而增加, 受带隙, 耗尽层长度和偏置电压的影响, 最大的响应率约为103 A·W-1; 通过限制上栅压, 带隙等变量可以控制系统暗电流, 增大探测器的探测率, 最高探测率约为109 cm·Hz1/2·W-1。 多层石墨烯纳米带结构可以增强探测器对入射光的吸收, 提高探测器的灵敏度以及对弱光的探测能力, 实现对太赫兹到远红外波段入射光的有效探测, 探测性能远高于许多量子结构和窄带半导体结构的光电探测器。
石墨烯 纳米带 光电设备 探测 Graphene Nanorrbbons Photoelectric devices Detection 光谱学与光谱分析
2016, 36(12): 3811
清华大学 精密仪器系精密测试技术与仪器国家重点实验室,北京 100084
本文讨论了利用激光频率分裂技术测量波片位相延迟的主要误差因素,并对其中激光器初始位相延迟和波片非对正引入的系统误差进行补偿。误差分析表明:系统对于多级波片的测量不确定度约为1.7′,对于零级波片为0.8′。然后针对系统性能进行实验评价,包括:比较波片沿激光轴线对正和倾斜时对测量结果的显著影响,以及测量波片通光面内不同点的位相延迟和波片光轴与其表面的夹角。根据实测结果,系统测量重复性和复现性优于0.02°,不确定度优于2′,即约λ/104。
波片 He-Ne 激光器 频率分裂 位相延迟 wave plate He-Ne laser frequency splitting phase retardation





